The Cytoskeleton
In ordinary preparations of visible light microscopy or electronic, the cytoskeleton appears transparent and therefore invisible. Generally not as drawn in the schemes of the cell but is an important cellular component, complex and dynamic. The cytoskeleton maintains the shape of the cell, "anchor" the organelles in place and move part of the cell processes of growth and mobility.
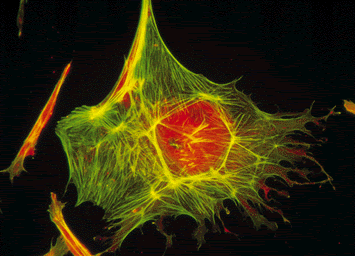
various types of protein filaments that constitute the cytoskeleton: microfilaments, microtubules and intermediate filaments.
The microtubules are composed of subunits of a protein called tubulin and are often used by the cell to maintain its shape, are also the largest component of cilia and flagella.
The microfilaments are composed of subunits of the protein actin. They are about one third the diameter of the microtubule and are often used by the cell to change its structure so as to maintain it.
A large number of proteins associated with the cytoskeleton that control its structure both through the guidance and direction of the filaments and groups of their movement. A particularly interesting group of proteins associated with the cytoskeleton are "other" phones, such as myosin (an "engine" that moves actin filaments) and kinesin (a "motor" for microtubule).
The three components cytoskeleton are interconnected and form a lattice, which extends from the cell surface to the core. This system is built on a common architectural model is in an amazing variety of natural systems and is known as tensional integrity (tensegrity). This expression indicates that the system stabilizes itself mechanically, because of how the compression and tension forces are distributed and balanced within the structure.
structures that respond to this model of tensional integrity not reach mechanical stability and resistance of individual members but by the way the whole structure distributes and balances mechanical stresses. In these structures the tension is transmitted seamlessly through all elements estructurales.En other words, an increase of stress in any element of the structure is felt in all others. This overall increase in pressure is balanced by an increase in the compression of certain elements all over the structure. An archetypal example of these structures are geodesic domes Buckminster Fuller.
should be noted that the universal rules governing the construction applies to the formation of organizational structures, from molecules to tissues.
Centrioles and Basal Bodies.
are basically the same thing, are interconvertible structures. A centriole is made up of nine bundles of microtubules triplets. A triplet contains a complete microtubule fused to two incomplete. The basal bodies are related with cilia and flagella where, as centrioles, are associated with the cytoskeleton.
Centrioles play a vital role in cell division. They are surrounded by a dense material that stains the pericentriolar material , from which microtubules originate, even in cells without centrioles microtubules originating from this material.
Centrioles are often known for their role in cell division. They are members of the centrosome consisting of two perpendicular centrioles. The centrioles appear to determine the position of material pericentriolar, which in turn affects cell polarity. Note that the functional centrosome is typically from an embryo sperm fertilizing.
To expand on this topic see this literature.
Cytoskeleton Tutorial
Microtubules, microfilaments and intermediate filaments
The cytoskeleton
http://www.biologia.arizona.edu/cEll/tutor/cyto/page1.html
Cytoskeleton
http://www2.uah.es/biologia_celular/LaCelula/Cel5CK.html
http://cancerquest.org/index.cfm?page=46 & ; lang = English & English CHANGETABLE =
Cell Biology Manual
http://w3.cnice.mec.es/eos/MaterialesEducativos/mem2001/biologia/citoplasma/esqueleto.htm
interaction between actin and other molecules, such as myosin -




0 comments:
Post a Comment